CHAPTER 9
APPLICATIONS OF LIFE INSURANCE
Chapter Introduction
Life insurance does not merely seek to protect individuals from premature death. It has other applications as well. It can be applied to the creation of trusts with resultant insurance benefits; it can be applied for creating a policy covering key personnel of industries and also for redeeming mortgages. We shall briefly describe these various applications of life insurance.
Learning Outcomes
A. Applications of life insurance
A. Applications of life insurance
1. Married Women’s Property Act
The concept of Trusts in a life policy is necessitated by the applicability of estate duty on transfer/inheritance of benefits under a life insurance policy, including annuities. While with the abolition of estate duty in India, the concept of Trusts may no longer be preferred, it is beneficial to understand the subject in detail.
Section 6 of the Married Women’s Property Act, 1874 provides for security of benefits under a life insurance policy to the wife and children. Section 6 of the Married Women’s Property Act, 1874 also provides for creation of a Trust.
Diagram 1: Beneficiaries under MWP Act
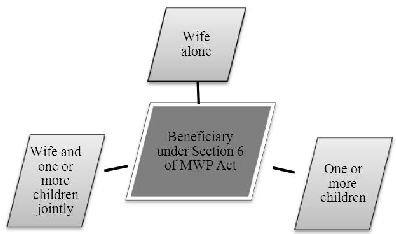
It lays down that a policy of insurance effected by any married man on his own life, and expressed on the face of it to be for the benefit of his wife, or of his wife and children, or any of them, shall ensure and be deemed to be a trust for the benefit of his wife, or of his wife and children, or any of them, according to the interest so expressed, and shall not, so long any object of the trust remains, be subject to the control of the husband, or to his creditors, or form part of his estate.
a) Features of a policy under the MWP Act
i. Each policy will remain a separate Trust. Either the wife or child (over 18 years of age) can be a trustee.
ii. The policy shall be beyond the control of court attachments, creditors and even the life assured.
iii. The claim money shall be paid to the trustees.
iv. The policy cannot be surrendered and neither nomination nor assignment is allowed.
v. If the policyholder does not appoint a special trustee to receive and administer the benefits under the policy, the sum secured under the policy becomes payable to the official trustee of the State in which the office at which the insurance was effected is situated.
b) Benefits
The Trust is set-up under an irrevocable, non-amendable Trust Deed and can hold one or more insurance policies. It is important to appoint a trustee for administration of the Trust property, being the benefits under the life policy. By creating a Trust to hold the insurance policies, the policyholder gives up his rights under the policy and upon the death of the life insured. The trustee invests the insurance proceeds and administers the Trust for one or more beneficiaries.
While it is a practice to create the Trust for the benefit of the spouse and children, the beneficiaries can be any other legal person. Creating a Trust ensures that the policy proceeds are invested wisely during the minority of the beneficiary and also secures the benefits against future creditors.
2. Key man Insurance
Keyman insurance is an important form of business insurance.
Definition
Keyman Insurance can be described as an insurance policy taken out by a business to compensate that business for financial losses that would arise from the death or extended incapacity of an important member of the business.
To put it simply, key man insurance is a life insurance that is used for business protection purposes. The policy's term does not extend beyond the period of the key person’s usefulness to the business. Key man insurance policies are usually owned by the business and the aim is to compensate the business for losses incurred with the loss of a key income generator and facilitate business continuity. Keyman insurance does not indemnify the actual losses incurred but compensates with a fixed monetary sum as specified on the insurance policy.
Many businesses have a key person who is responsible for the majority of profits, or has a unique and hard to replace skill set such as intellectual property that is vital to the organisation. An employer may take out a key person insurance policy on the life or health of any employee whose knowledge, work, or overall contribution is considered uniquely valuable to the company.
The employer does this to offset the costs (such as hiring temporary help or recruiting a successor) and losses (such as a decreased ability to transact business until successors are trained) which the employer is likely to suffer in the event of the loss of a key person.
Keyman is a term insurance policy where the sum assured is linked to the profitability of the company rather than the key person’s own income. The premium is paid by the company. This is tax efficient as the entire premium is treated as business expense. In case the key person dies, the benefit is paid to the company. Unlike individual insurance policies, the death benefit in keyman insurance is taxed as income.
The insurer will look at the business’ audited financial statements and filed IT returns in assessing the sum assured. Generally, the company must be profitable to be eligible for keyman insurance. In a few cases, insurers make exceptions for loss making but well-funded start-up companies.
a) Who can be a keyman?
A key person can be anyone directly associated with the business whose loss can cause financial strain to the business. For example, the person could be a director of the company, a partner, a key sales person, key project manager, or someone with specific skills or knowledge which is especially valuable to the company.
b) Insurable losses
The following losses are those for which key person insurance can provide compensation:
i. Losses related to the extended period when a key person is unable to work, to provide temporary personnel and, if necessary to finance the recruitment and training of a replacement
ii. Insurance to protect profits. For example, offsetting lost income from lost sales, losses resulting from the delay or cancellation of any business project that the key person was involved in, loss of opportunity to expand, loss of specialised skills or knowledge
3. Mortgage Redemption Insurance (MRI)
Suppose you are taking a loan to buy a property. You may be required to pay for mortgage redemption insurance by the bank as part of the loan arrangement.
a) What is MRI?
It is an insurance policy that provides financial protection for home loan borrowers. It is basically a decreasing term life insurance policy taken by a mortgagor to repay the balance on a mortgage loan if he/she dies before its full repayment. It can be called a loan protector policy. This plan is suitable for elderly people whose dependents may need assistance in clearing their debts in case of the unexpected demise of the policyholder.
b) Features
The policy bears on surrender value or maturity benefits. The insurance cover under this policy decreases each year unlike a term insurance policy where insurance cover is constant during the policy period.
Test Yourself 1
What is the objective behind Mortgage Redemption Insurance?
I. Facilitate cheaper mortgage rates
II. Provide financial protection for home loan borrowers
III. Protect value of the mortgaged property
IV. Evade eviction in case of default
Summary
• Section 6 of the Married Women’s Property Act, 1874 provides for security of benefits under a life insurance policy to the wife and children.
• The policy effected under MWP Act shall be beyond the control of court attachments, creditors and even the life assured.
• Keyman insurance is an important form of business insurance. It can be described as an insurance policy taken out by a business to compensate at for financial losses that would arise from the death or extended capacity of an important member of the business.
• Mortgage redemption insurance is basically a decreasing term life insurance policy taken by a mortgagor to repay the balance on a mortgage loan if he/she dies before its full repayment.
Key Terms
1. Married Women’s Property Act
2. Keyman insurance
3. Mortgage Redemption Insurance
